Неэргодическая экономика
Авторский аналитический Интернет-журнал
Изучение широкого спектра проблем экономики
Статьи
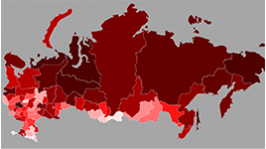
В статье проведен анализ влияния международных санкций на экономику России с целью выявления и оценки их позитивного эффекта. На статистических данных и стилизованных примерах показан ряд экономических направлений, где произошло заметное оздоровление ситуации и были заложены созидательные основы отечественного производства. На примере изменений географической и товарной структуры товарооборота показаны возможности России по диверсификации торговых рынков, наращиванию внешнеторгового сотрудничества с новыми контрагентами, а также повышению продовольственной безопасности страны. Рассмотрены положительные тренды в импортозамещении в таких отраслях как сельское хозяйство, военно–промышленный комплекс, ИТ–индустрия. Помимо этого, приведены примеры, демонстрирующие возможности России в совершении технологического прорыва, необходимого для ее дальнейшего развития. В заключении резюмируются положительные аспекты влияния санкций, а также делается вывод о необходимости обращения в сторону внутреннего потенциала страны, поиска скрытых резервов и возможностей.
09.01.2019
В автореферате представлено краткое описание основных результатов диссертационного исследования. Особое внимание уделено характеристике переходного периода, а также взаимосвязи экономического роста и инфляционных налогов, экономического роста и эффекта Оливейры–Танзи, особенностям формирования спроса и предложения для различных товаров и производств, динамике мультпликатора инвестиций и другим макроэкономическим темам.
30.12.2018
В статье дается обзор исследований неравномерности развития экономического пространства России. Эта проблема имеет, по крайней мере, два измерения – неравномерность распределения доходов по группам населения и неравномерность развития регионов страны. В обзоре дается анализ причин усиления дифференциации развития регионов в разных странах мира, включая особенности регионального развития России. Показано, что объективные различия в экономическом положении регионов отрицают унифицированную политику в отношении их регулирования.
29.12.2018
В статье рассматривается общее правило инвестирования в новые проекты (производства), которое описывается кумулятивным уравнением равновесия из теории технологических ловушек. Показано влияние ставки дисконта на принимаемые инноватором решения относительно внедрения нового варианта развития бизнеса. Доказывается, что роль дисконта неоднозначно влияет на условия инвестирования; приводятся результаты вычислительных экспериментов.
25.12.2018
В статье рассмотрена проблема выбора одного из четырех проектов реформы подоходного налогообложения – трех политический фракций (партия «Справедливая Россия», ЛДПР и КПРФ), выступающих за введение прогрессивной шкалы подоходного налога, и Правительства Российской Федерации, предлагающего повысить ставку плоской шкалы с 13 до 15%. Каждый из указанных сценариев характеризуется риском невыполнения, что должно быть учтено при построении системы приоритетов в отношении имеющихся проектов налоговой реформы. В статье предлагается процедура анкетного опроса, позволяющая получить экспертные оценки степени реализуемости рассматриваемых проектов. Авторы предлагают обобщенный критерий результативности проекта реформы в мультипликативной форме, который предполагает учет его потенциального фискально-социального эффекта и уровня надежности.
18.12.2018
В статье рассматриваются основные этапы становления малого бизнеса в России, дается оценка масштабов и эффективности его деятельности. На базе проведенных расчетов показано влияние развития малого предпринимательства на темпы экономического спада в 90-х годах. Критически оцениваются макроэкономические подходы к стимулированию деятельности малых предприятий. Намечены основные пути развития отечественного малого бизнеса.
13.12.2018
В статье предлагается оригинальная методика оценки ущерба от законодательной деятельности федерального правительства в регионе. Методика представляет собой простую процедуру расчета, основанную на использовании принципа мультипликатора. Продолжением методики является схема расчета компенсационных выплат федерального центра региону, понесшему ущерб. На условном примере показано применение разработанной методики.
11.12.2018
В статье рассматривается простая диффузионная модель роста нового рынка, в которую вводится дополнительный фактор – налоговая нагрузка. Такая модель позволяет понять долгосрочное влияние фискального фактора, который предопределяет асимпотические свойства объема рынка нового продукта и оказывает нелинейное воздействие на активность предприятия-инноватора. На условном примере проиллюстрированы возможности применения предложенной модели в прикладных расчетах.
11.12.2018
В статье рассматриваются тенденции реструктуризации промышленности по формам собственности и их влияние на темпы роста (падения) промышленного производства. Дан сравнительный анализ функционирования предприятий различных форм собственности. Проанализирована тенденция разукрупнения промышленных предприятий и тренд по выравниванию производительности труда производственных объектов различных форм собственности.
10.12.2018
В статье углубляется и уточняется один из тезисов теории институциональных ловушек, согласно которому экономический рост в условиях смешанных институциональных стратегий возможен только при явном доминировании одного из институтов. Показано, что изначальный тезис действует как для институциональных, так и для технологических укладов компаний. В модельных построениях автора снимаются некоторые априорные ограничения, что позволяет продемонстрировать универсальность тезиса о влиянии институтов и технологий на экономический рост.
06.12.2018